Robert Schumann was one of the leading figures of classical music’s Romantic Era. His music – by turns tempestuous and ecstatic and always heartfelt – made a huge impression not only on audiences but on his fellow composers, too.
Today, we’re looking at seven works that Robert Schumann’s friends and colleagues wrote as tributes to him and his genius.
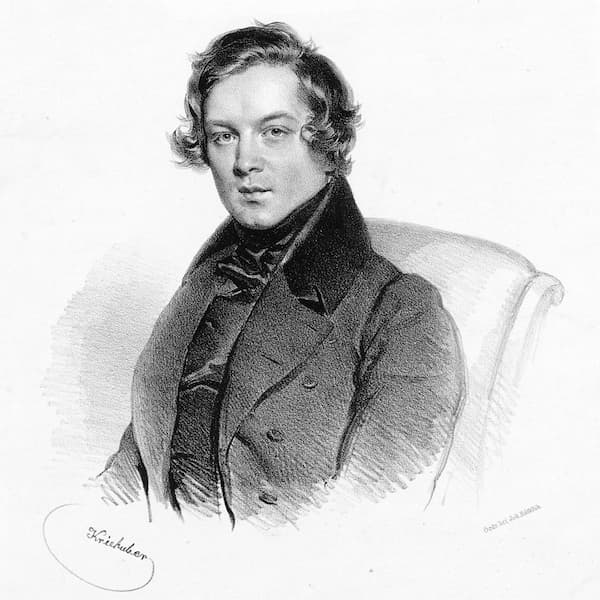

Josef Kriehuber: Robert Schumann, 1839
Frédéric Chopin: Ballade No. 2 (1836-39)
Frédéric Chopin and Robert Schumann had a bit of an awkward relationship. Schumann raved about Chopin’s music in his music journalism, but Chopin seems to have had a cooler opinion about Schumann’s work.
They met twice. The first time was in 1835 when Chopin was passing through Leipzig after visiting his parents. Schumann wrote about the encounter with great enthusiasm in his diary, but if Chopin ever recorded his impressions of the meeting, such an account hasn’t survived.
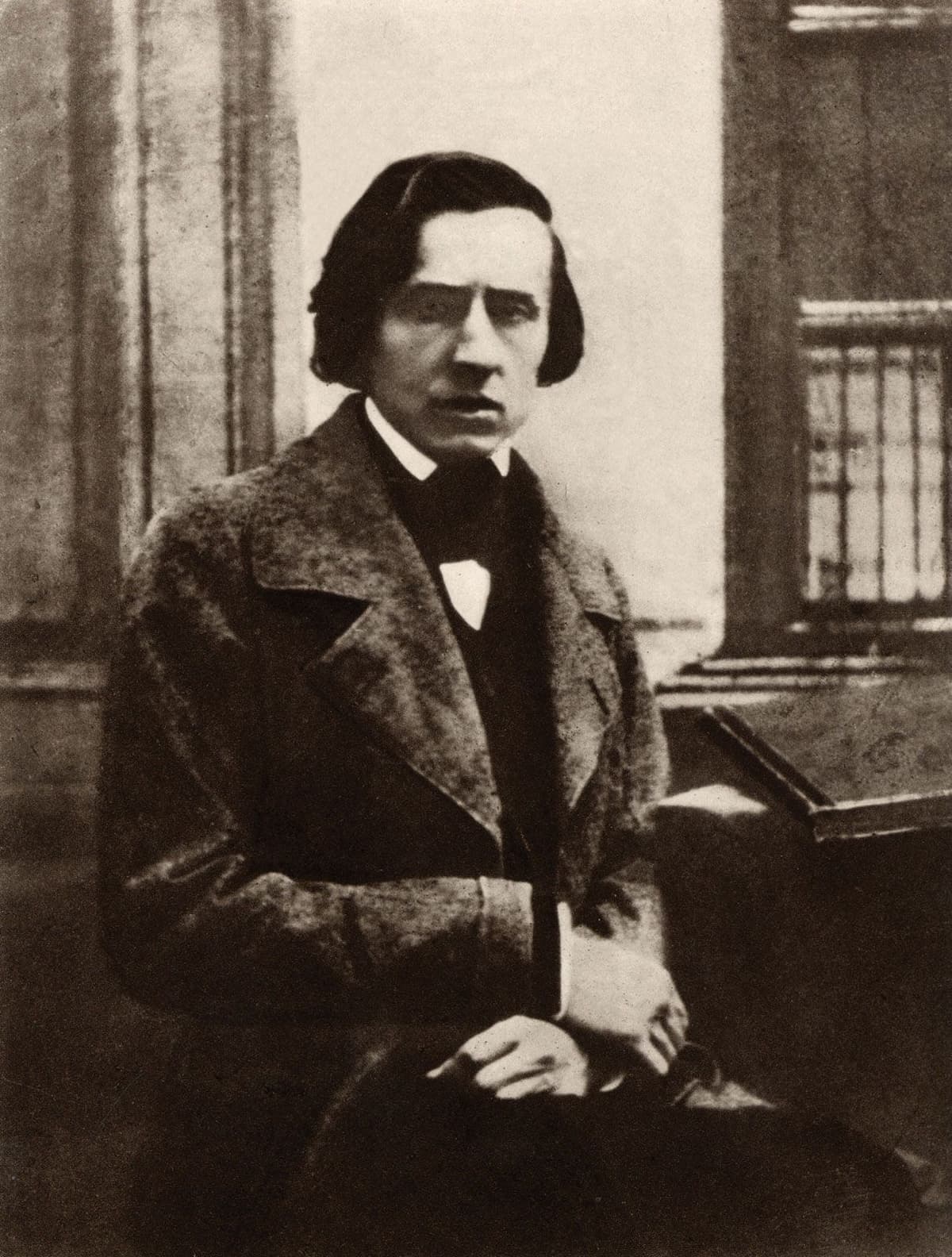

Frédéric Chopin
The second and final time was in 1836. Schumann tried initiating the meeting via letter but got no response. Then, one day, he arrived home to find Chopin waiting at his doorstep! They played music for one another, and Robert’s soon-to-be-wife Clara Wieck joined them.
After the visit, Schumann dedicated his Kreisleriana to Chopin, calling him “my friend” on the dedication page. Chopin reciprocated by dedicating this Ballade to Schumann…but was much more formal, dedicating it to “Mr. Robert Schumann,” and (perhaps pointedly) making no mention of friendship.
William Sterndale Bennett: Fantaisie, Op.16 (1837)
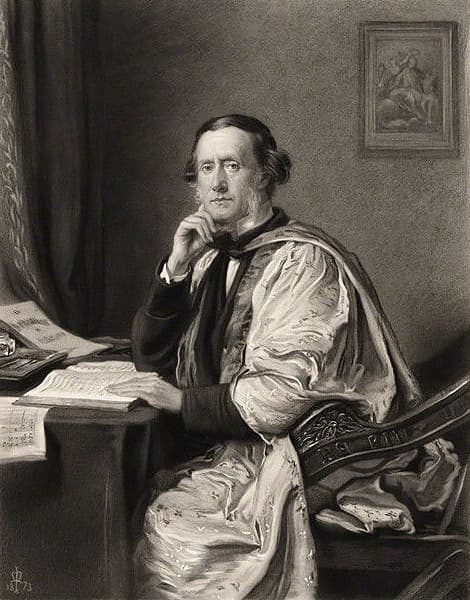
William Sterndale Bennett was a British pianist, composer, and conductor who was born in 1816.
He began composing at an early age, and several big names in European music were very impressed by him. Felix Mendelssohn invited the young man to Leipzig, where he met Robert Schumann. All three men deeply admired each other’s work.

William Sterndale Bennett
In 1837, the year he turned twenty-one, Bennett began teaching at the Royal Academy of Music in London. He also wrote this four-movement “Fantaisie” for solo piano and dedicated it to his friend and mentor Robert Schumann.
Clara Wieck Schumann: 3 Romances, Op.11 (1839)
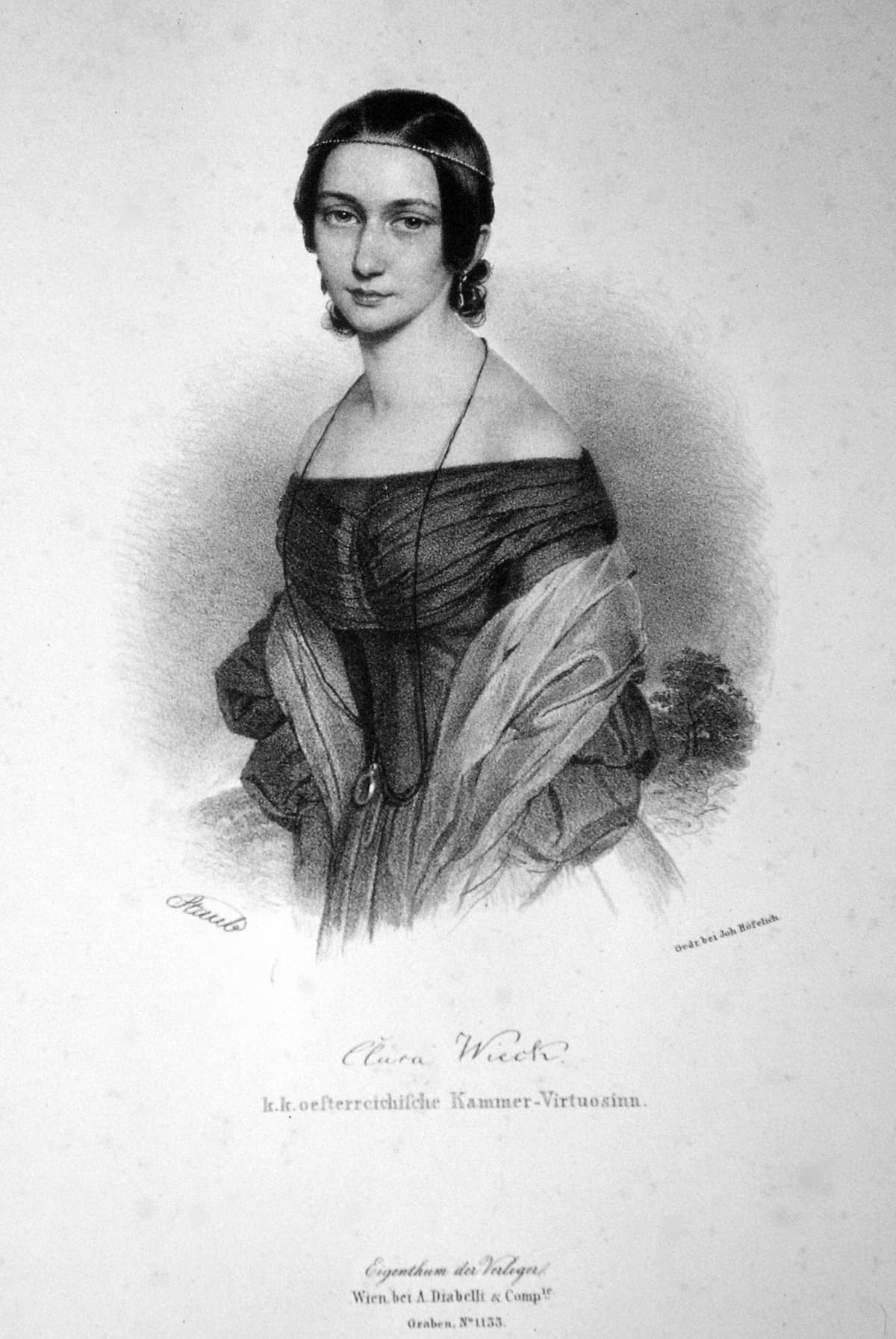
Robert Schumann admired many composers, but the one he loved the most was his girlfriend and later wife, Clara Wieck Schumann, who he married in September 1840, a day before her twenty-first birthday.

Andreas Staub: Clara Wieck, 1839
Their courtship was stormy. Her father disapproved of the match and went to court to try to prevent it. There were periods of time when the two were separated against their wills or when Clara was away concertising in the capitals of Europe. But they always found their way back to each other.
It is tempting to read her longing for Robert into these three-yearning works for solo piano that she dedicated to him in 1839, the year before their marriage.
Ignaz Moscheles: Cello Sonata No. 2 (1850-51)
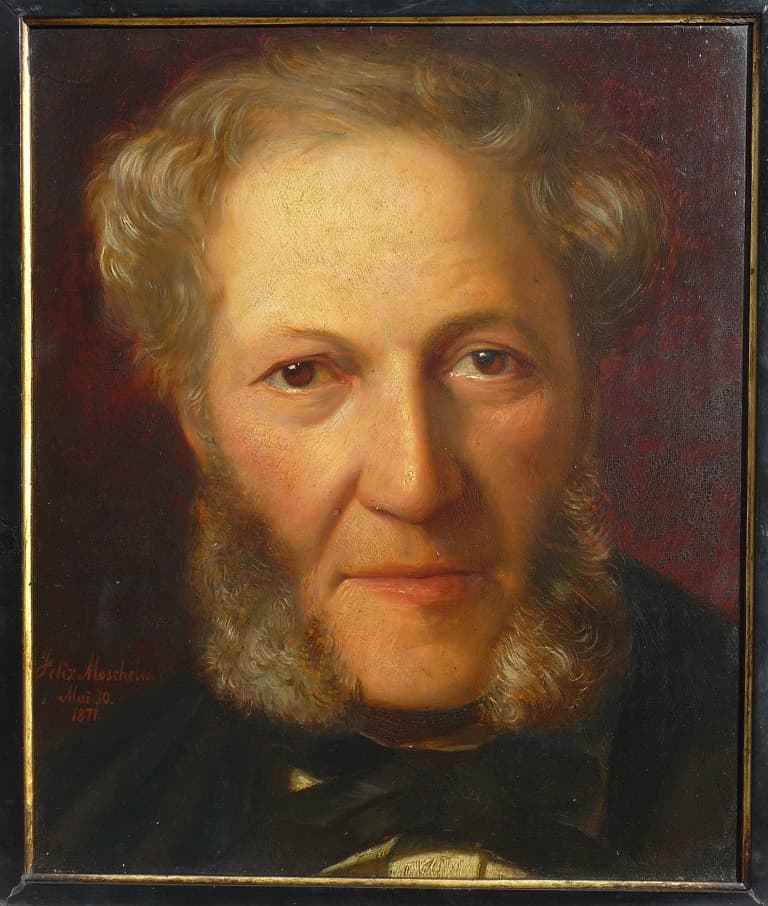
Ignaz Moscheles was born in 1794 in Prague. He was a talented pianist and composer, and was one of the earliest champions of the music of Beethoven.
As a young man, he made sensational impressions on audiences touring through Europe. One of the listeners particularly affected by his piano playing was none other than Robert Schumann.

Ignaz Moscheles
Moscheles enjoyed a great friendship with the Mendelssohn family due to their Jewish heritage, passion for music, and Moscheles’s acknowledgement of Mendelssohn’s genius. Moscheles and the Mendelssohns were also friends with the Schumanns. (Moscheles even played a three-harpsichord concerto with Clara Schumann once – an unusual sight in the mid-nineteenth century!)
Given their overlapping friendships, it makes sense that Moscheles dedicated this charming Romantic cello sonata to Robert Schumann.
Woldemar Bargiel: Piano Trio No. 1 (1851)
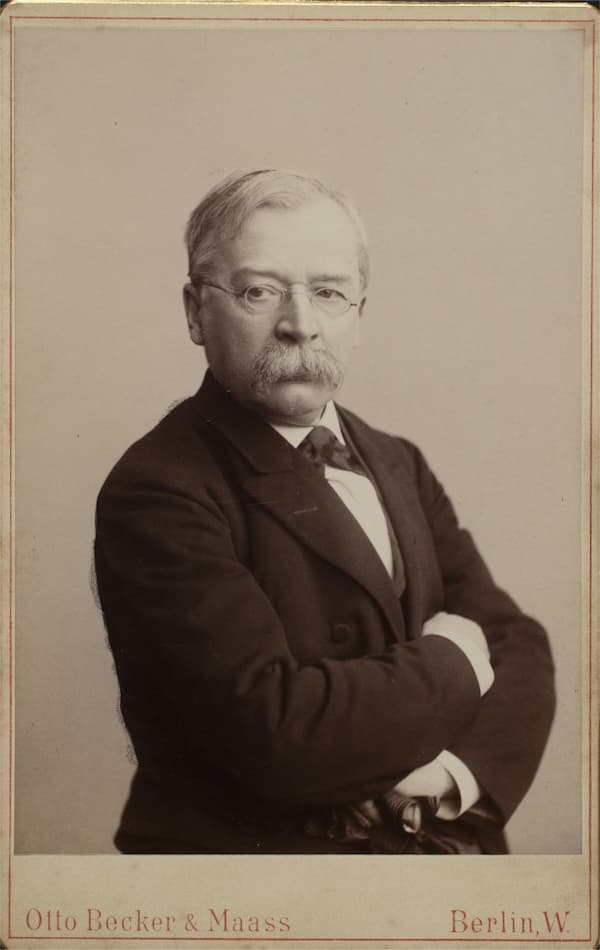
German composer Woldemar Bargiel’s origin story was complicated.
Bargiel’s mother Mariane Tromlitz was a professional singer. In 1816, she married a demanding piano teacher named Friederich Wieck and had five children with him, among them a prodigy pianist named Clara.
In 1824, unable to endure her marriage any longer, Mariane divorced Wieck and (awkwardly) married Wieck’s best friend Adolphe Bargiel instead. She eventually had three more children with Adolphe, including Woldemar.

Woldemar Bargiel
It worked out well for the young and musical Woldemar to have a brilliant half-sister pianist nine years his senior. She gave career advice and provided him introductions to giants like Mendelssohn and Schumann. Their social circle suggested that he study at the Leipzig Conservatory, which he did between the ages of eighteen and twenty.
In 1848, he moved to Berlin to pursue his career there. This piano trio was written in 1851 and was unpublished for five years until Robert and Clara Schumann worked their connections so that it could be printed. In gratitude, he dedicated it to Robert.
Franz Liszt: Piano Sonata in B-minor (1852-53)
Clara Wieck Schumann and Franz Liszt had a rocky professional relationship. It started out positively. When she was a young girl, she was awed by his virtuosity, and for his part, Liszt found her compositions impressive, “especially for a woman,” as he reported to his partner, Marie d’Agoult.
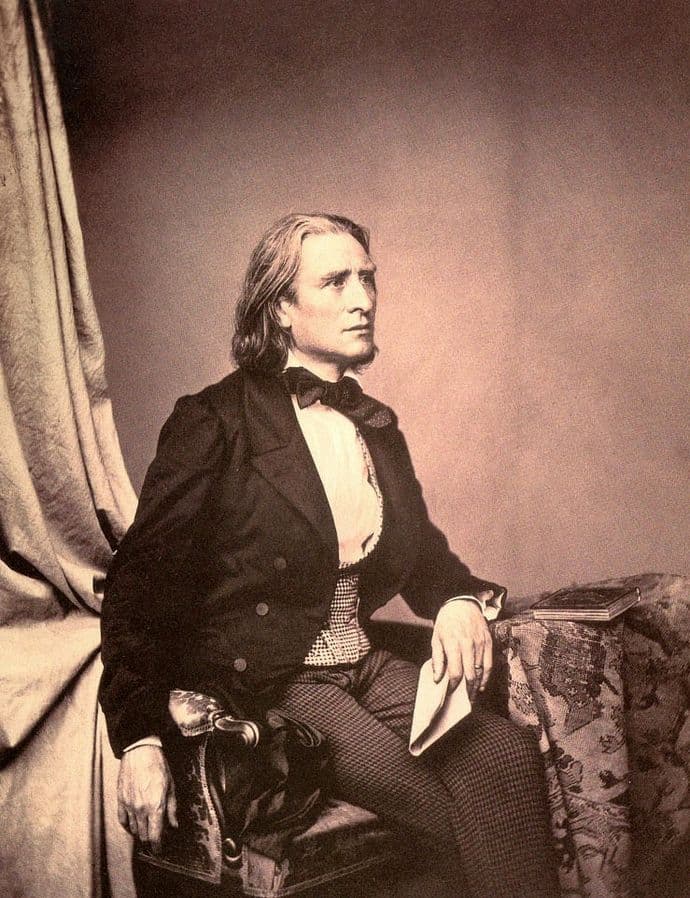

Franz Hanfstaengl: Franz Liszt, 1858
But as the years went on, Clara became more and more leery of his brash style and willingness to depart from the score.
An all-out feud erupted in 1848 when Liszt called Robert Schumann’s Piano Quintet “typically Leipzig”, which insulted Clara. But Robert smoothed things over, to Clara’s irritation; in her artistic maturity, she didn’t want anything to do with Liszt’s style of music-making.
In 1854, Liszt published this piano sonata and dedicated it to Robert Schumann. Not surprisingly, Clara had a strong reaction, writing in her journal:
Today, Liszt sent me a Sonata dedicated to Robert and some more pieces, together with a polite note. But those pieces are so creepy! Brahms played them to me and I felt really miserable … This is only blind noise – no more healthy thoughts, everything is confused, one cannot see any clear harmonies! And, what is more, I still have to thank him now – this is really awful.
Despite her disgust, Liszt cheerfully retained his admiration for her music and her playing.
Clara Wieck Schumann: Variationen über ein Thema von Robert Schumann, Op.20 (1853)
It’s fitting that the final work on this list is another one of Clara’s.
This set of variations on a theme originally composed by Robert was written as his 41st birthday present. She wrote it in less than a week.
In this work, Clara includes references to multiple pieces of music by her husband, herself, and Felix Mendelssohn (who had died young and unexpectedly a few years before).
Eduard Magnus: Mendelssohn, 1846
It was one of the last musical projects they shared. Over the winter, Robert’s mental health deteriorated. In February 1854, he nearly died by suicide after jumping off a bridge into the Rhine River. It was determined that he needed to go to an asylum for his own safety. He died in the asylum in 1856. Clara would only be allowed to see him once more, shortly before his passing.
To comfort her, Johannes Brahms wrote his own variations for Clara based on this work after Robert had been institutionalised. It may not be dedicated to Robert officially, but it certainly was dedicated to him in spirit, so here it is as a bonus. We wrote about it here.
For more of the best in classical music, sign up for our E-Newsletter


