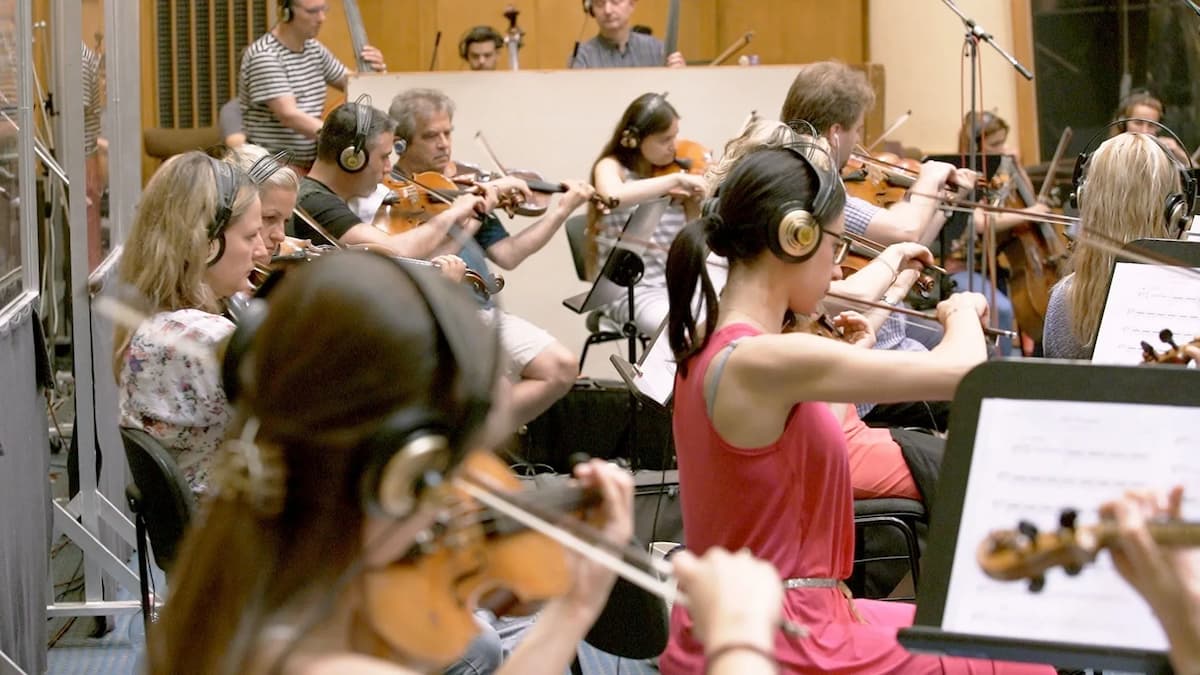Recording Film and TV Music Behind-the-Scene
Cast your mind back to the last movie or TV show you watched. Chances are there was music of some kind, enhancing the mood, providing suspense at cliffhangers, setting the scene or underscoring a poignant moment. Wherever we look in the media, music is everywhere, but did you ever wonder who exactly plays the instruments on these recordings, or how the process works?
You’d be forgiven for not giving it a second thought; music for media, after all, is there to enhance the overall experience, and arguably is most effective when it doesn’t stick out too much. There is, however, a whole industry behind recording live musicians and getting music ready for picture.
In a place like London, recording studios can be found all over the city, ranging from humble setups in converted warehouses to grand institutions with international reputations, like Abbey Road and AIR Studios.
The studios themselves don’t employ musicians. This job is outsourced to external booking agents, known as ‘fixers’. The musicians in the fixers’ books often have heaps of experience and are some of the best players in their field. The pace of recordings is fast and high-pressured, so being engaged for a recording session requires you to be at the top of your game. In London, session musicians can also be found freelancing in orchestras, in shows on the West End, touring with chamber groups – for many musicians, session work makes up just one part of their career.
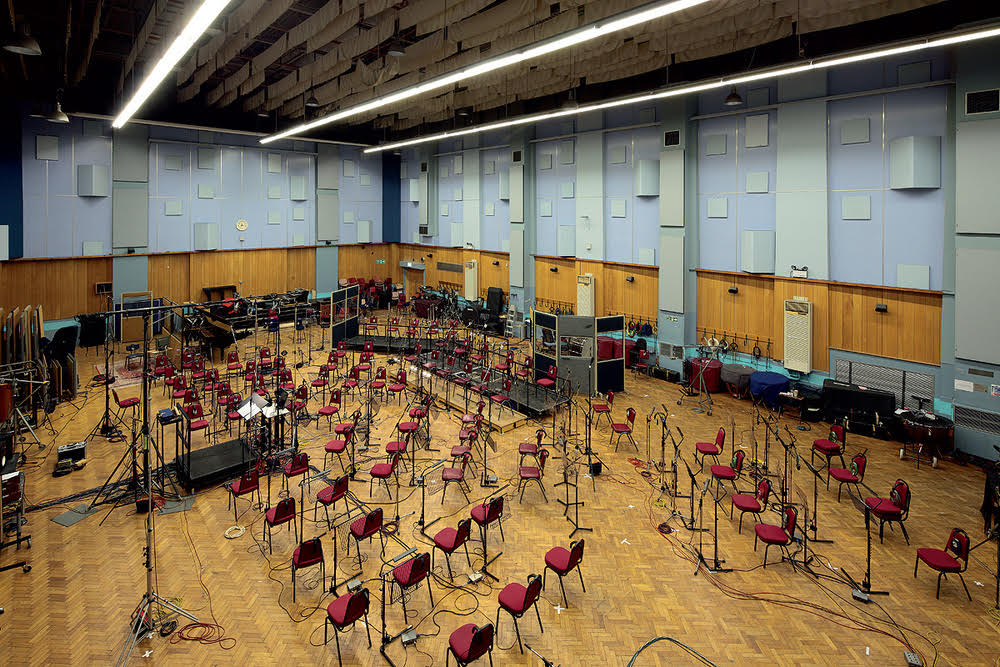

Abbey Road Studio One: The world-famous studio where many film soundtracks have been recorded, including the soundtracks to the Lord of the Rings trilogy and The Empire Strikes Back
One of the great things about doing recording sessions as a classical musician is the variety of music you come into contact with. I’ve been in orchestras and ensembles recording music for films, TV dramas, nature documentaries, pop albums, art house movies… the range is so broad, and it keeps the work endlessly interesting.
For film and TV, we musicians come into the production process relatively late. A movie’s soundtrack isn’t finalised until pretty much the final edit, seeing as scores and parts have to be made for a large number of people. Changing and editing orchestral scores is a time-consuming (and costly) process, so it’s often left as late as possible in order that (hopefully) the music can simply be recorded and lined up with finalised visuals that won’t change much if at all, to avoid costly adjustments to the soundtrack.
Of course, there is the magic of editing (it is possible to record a whole orchestra and then chose and change it at your whim) but broadly speaking, recording sessions happen mostly towards the end of production, rather than the beginning, and there is something exciting about being part of a process much bigger than yourself. Sometimes there are screens in the studio that playback footage as you’re recording, and to see the show coming to life in real-time can be quite thrilling.
Not every soundtrack you will have heard will have been recorded live, however. The landscape of recordings has changed dramatically in recent decades, spurred on by huge advances in technology. As software has become more and more sophisticated, commercial ‘sound libraries’ have flooded the market, letting composers create incredibly realistic-sounding scores just by using a bank of prerecorded sounds.
While these can be incredibly useful, enabling productions without the budget to accommodate live orchestral setups to achieve realistic-sounding results, there is still very much a place for live recording, and it is still very much part of the production process for many TV shows, movies, video games and other soundtracks.
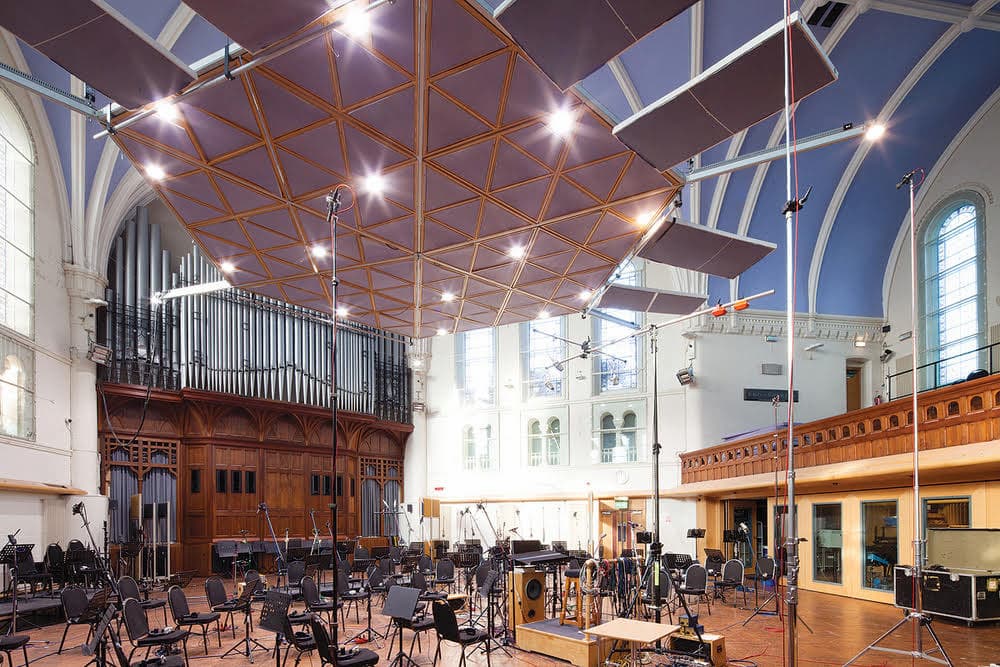

AIR Studios Exterior: The outside of Abbey Road’s less well-known cousin, AIR Studios. You’d be forgiven for walking past
without even realising it’s there; AIR has had many previous bases, but this converted church has been its home since 1992.
The level of responsiveness and adaptation you can request of professional musicians is something that, in my opinion, cannot be equaled by any sound bank. It’s commonplace in sessions to be asked to play several takes in a different way – the director or music supervisor might want it to sound more angry, or calm, or glassy, excited, soulless… the list goes on. That is much easier to achieve with a human being who can respond on the spot rather than having to recalibrate a preset batch of sounds.
Session work, while sometimes stressful, can be incredibly rewarding. It may take a while to get into that particular world, at least in the UK, but it offers interesting and challenging opportunities that can fit nicely into a freelancing career.
Ever wondered what actually happens in a recording session, or how different they are from a live performance? Read on to discover more…
For more of the best in classical music, sign up to our E-Newsletter
Film Music Documentary